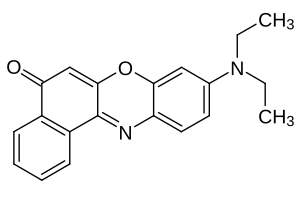
Nilrot
| Strukturformel | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | |||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Nilrot | ||||||||||||||||||
| Andere Namen |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C20H18N2O2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung |
dunkelgrüner Feststoff[1] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 318,37 g·mol−1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
fest | ||||||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt | |||||||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen (0 °C, 1000 hPa). | |||||||||||||||||||
Nilrot, auch als Nilblau-Oxazon bezeichnet, ist ein lipophiler fluoreszierender Phenoxazin-Farbstoff.
Herstellung
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]Nilrot entsteht durch Kochen einer Lösung von Nilblau mit Schwefelsäure. Dabei wird die Aminogruppe durch eine Carbonylgruppe ersetzt.
Eigenschaften und Verwendung
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]
V. l. n. r.: 1. Wasser, 2. Methanol, 3. Ethanol, 4. Acetonitril, 5. Dimethylformamid, 6. Aceton, 7. Ethylacetat, 8. Dichlormethan, 9. n-Hexan, 10. tert-Butylmethylether, 11. Cyclohexan, 12. Toluol.
Nilrot ist ein hochfluoreszierender Laser-Farbstoff.[2] Es fluoresziert im roten Bereich bis in das Nahinfrarot (NIR)[3] hinein und hat ein Emissionsmaximum bei etwa 650 nm.[4] Sowohl das Emissionsmaximum, als auch die Quantenausbeute, sind vom verwendeten Lösungsmittel stark abhängig. In n-Heptan liegt das Emissionsmaximum bei etwa 520 nm, in Aceton dagegen bei 600 nm. Dabei ist die Fluoreszenz in Aceton etwa 80-mal schwächer.[5] Eine höhere Polarität des Lösungsmittel führt generell zu einer Rotverschiebung des Fluoreszenzmaximums und zu einer Abnahme der Quantenausbeute und der Fluoreszenzlebensdauer von Nilrot.[6]
In der Mikrobiologie wird Nilrot zum Markieren und Anfärben (engl. Staining) von Zellen beziehungsweise Zellbestandteilen verwendet. Die Fluoreszenz ist dabei von der Hydrophobie der Lipide abhängig. Polare, das heißt hydrophilere Lipide, wie beispielsweise Phospholipide, die sich im Wesentlichen in der Zellmembran befinden, fluoreszieren rot. Neutrale Fette, wie beispielsweise Triglyceride oder Cholesterinester in intrazellulären Fetttröpfchen, fluoreszieren dagegen bei kürzeren Wellenlängen (in Richtung Gelb).[7] Die Fluoreszenz kann dabei sowohl mikroskopisch, als auch mittels Durchflusszytometrie gemessen werden.[5]
Nilrot wird in der Biochemie zur Färbung von Proteinen im Zuge einer Proteincharakterisierung verwendet, z. B. bei der SDS-PAGE und der isoelektrischen Fokussierung.[8][9]
Einzelnachweise
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]- ↑ a b c d Datenblatt Nile Red, suitable for fluorescence, BioReagent, ≥98.0% (HPLC) bei Sigma-Aldrich, abgerufen am 18. November 2019 (PDF).
- ↑ H. Tajalli u. a.: The photophysical properties of Nile red and Nile blue in ordered anisotropic media. In: Dyes and Pigments 78, 2008, S. 15–24.
- ↑ J. N. Lampe u. a.: Nile Red is a fluorescent allosteric substrate of cytochrome P450 3A4. In: Biochemistry 47, 2008, S. 509–516. PMID 18092806
- ↑ S. D. Fowler u. a.: Use of nile red for the rapid in situ quantitation of lipids on thin-layer chromatograms. In: J Lipid Res 28, 1987, S. 1225–1232. PMID 3681147
- ↑ a b P. Greenspan u. a.: Nile red: a selective fluorescent stain for intracellular lipid droplets. In: J Cell Biol 100, 1985, S. 965–973. PMID 3972906.
- ↑ M. Sutter u. a.: Sensitive spectroscopic detection of large and denatured protein aggregates in solution by use of the fluorescent dye Nile red. In: Journal of Fluorescence 17, 2007, S. 181–192. PMID 17294134; PMC 1915606 (freier Volltext).
- ↑ G. Diaz u. a.: Hydrophobic characterization of intracellular lipids in situ by Nile Red red/yellow emission ratio. In: Micron 39, 2008, S. 819–824. PMID 18329888
- ↑ A. Bermudez, J. R. Daban, J. R. Garcia, E. Mendez: Direct blotting, sequencing and immunodetection of proteins after five-minute staining of SDS and SDS-treated IEF gels with Nile red. In: BioTechniques. Band 16, Nummer 4, April 1994, S. 621–624, PMID 8024781.
- ↑ F. J. Alba, S. Bartolomé, A. Bermúdez, J. R. Daban: Fluorescent labeling of proteins and its application to SDS-PAGE and western blotting. In: Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.). Band 536, 2009, S. 407–416, doi:10.1007/978-1-59745-542-8_41. PMID 19378078.
Weiterführende Literatur
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]- A. Nath u. a.: Spectral resolution of a second binding site for Nile Red on cytochrome P4503A4. In: Arch Biochem Biophys 474, 2008, S. 198–204. PMID 18395506.
- A. Rei u. a.: Nile Red Synchronous Scan Fluorescence Spectroscopy to Follow Matrix Modification in Sol-Gel Derived Media and its Effect on the Peroxidase Activity of cytochrome c. In: J Fluoresc 18, 2008, S. 1083–1091. PMID 18365305.
- G. Genicot u. a.: The use of a fluorescent dye, Nile red, to evaluate the lipid content of single mammalian oocytes. In: Theriogenology 63, 2005, S. 1181–1194. PMID 15710202.
- E. Bonilla und A. Prelle: Application of nile blue and nile red, two fluorescent probes, for detection of lipid droplets in human skeletal muscle. In: J Histochem Cytochem 35, 1987, S. 619–621. PMID 3559182.
- J. N. Lampe u. a.: Nile Red is a fluorescent allosteric substrate of cytochrome P450 3A4. In: Biochemistry 47, 2008, S. 509–516. PMID 18092806.
- J. Han u. a.: Chemiluminescent energy-transfer cassettes based on fluorescein and nile red. In: Angew Chem Int Ed 46, 2007, S. 1684–1687.PMID 17397078.
- K. Tainaka u. a.: Nile Red nucleoside: novel nucleoside analog with a fluorophore replacing the DNA base. In: Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 49, 2005, S. 155–156. PMID 17150680.
- S. Mukherjee u. a.: Membrane localization and dynamics of Nile Red: effect of cholesterol. In: Biochim Biophys Acta 1768, 2007, S. 59–66. PMID 16934217.
- M. L. Ferrer und F. del Monte: Enhanced emission of nile red fluorescent nanoparticles embedded in hybrid sol-gel glasses. In: J Phys Chem B 109, 2005, S. 80–86. PMID 16850987.
- K. J. Thomas u. a.: A long-wavelength fluorescent glucose biosensor based on bioconjugates of galactose/glucose binding protein and Nile Red derivatives. In: Diabetes Technol Ther 8, 2006, S. 261–268. PMID 16800747.
- K. Sebok-Nagy u. a.: Interaction of 2-hydroxy-substituted Nile red fluorescent probe with organic nitrogen compounds. In: Photochem Photobiol 81, 2005, S. 1212–1218. PMID 15901209.
- D. L. Sackett und J. Wolf: Nile red as a polarity-sensitive fluorescent probe of hydrophobic protein surfaces. In: Anal Biochem 167, 1987, S. 228–234. PMID 3442318.
- J. Jose und K. Burgess: Syntheses and properties of water-soluble Nile Red derivatives. In: J Org Chem 71, 2006, S. 7835–7839. PMID 16995693.
- A. Steinbüchel u. a.: Mikrobiologisches Praktikum. Verlag Springer, 2003, ISBN 3-540-44383-5, S. 384.
- A. Douhal: Cyclodextrin Materials Photochemistry, Photophysics and Photobiology. Verlag Elsevier, 2006, ISBN 0-444-52780-X, S. 49–50.