3-Ethylpentan
| Strukturformel | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

| ||||||||||||||||
| Allgemeines | ||||||||||||||||
| Name | 3-Ethylpentan | |||||||||||||||
| Summenformel | C7H16 | |||||||||||||||
| Kurzbeschreibung |
leichtentzündbare farblose Flüssigkeit[1] | |||||||||||||||
| Externe Identifikatoren/Datenbanken | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Eigenschaften | ||||||||||||||||
| Molare Masse | 100,21 g·mol−1 | |||||||||||||||
| Aggregatzustand |
flüssig | |||||||||||||||
| Dichte |
0,70 g·cm−3[1] | |||||||||||||||
| Schmelzpunkt | ||||||||||||||||
| Siedepunkt |
93 °C[1] | |||||||||||||||
| Dampfdruck |
235 mbar (50 °C)[1] | |||||||||||||||
| Löslichkeit |
praktisch unlöslich in Wasser[1] | |||||||||||||||
| Brechungsindex |
1,3934 (20 °C)[3] | |||||||||||||||
| Sicherheitshinweise | ||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||
| Soweit möglich und gebräuchlich, werden SI-Einheiten verwendet. Wenn nicht anders vermerkt, gelten die angegebenen Daten bei Standardbedingungen (0 °C, 1000 hPa). Brechungsindex: Na-D-Linie, 20 °C | ||||||||||||||||
3-Ethylpentan ist eine chemische Verbindung aus der Gruppe der aliphatischen gesättigten Kohlenwasserstoffe. Es ist eines der neun Konstitutionsisomere des Heptans.
Gewinnung und Darstellung
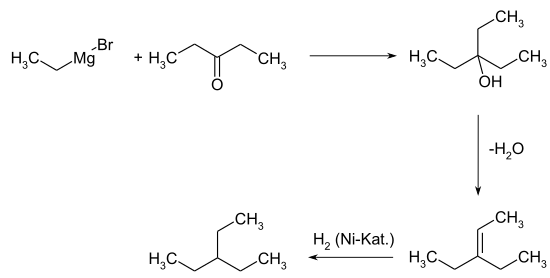
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]3-Ethylpentan kommt im Erdöl vor.[4] Die Verbindung kann in geringen Anteilen durch die Isomerisierung von n-Heptan erhalten werden.[5][6] Schon 1927 wurde eine Laborsynthese beschrieben, bei der die Grignardverbindung aus Ethylbromid mit 3-Pentanon umgesetzt wird. Das resultierenden 3-Ethyl-3-pentanol wird zum 3-Ethyl-2-penten dehydratisiert und anschließend mittels Nickelkatalysor zum 3-Ethylpentan hydriert.[7]
Eigenschaften
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]Physikalische Eigenschaften
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]3-Ethylpentan ist ein leichtentzündliche und farblose Flüssigkeit.[1] Die Dampfdruckfunktion ergibt sich nach Antoine entsprechend log10(P) = A−(B/(T+C)) (P in bar, T in K) mit A = 4,00453, B = 1254,119 und C = −53,004 im Temperaturbereich von 294 bis 364 K.[8]
Die wichtigsten thermodynamischen Eigenschaften sind in der folgenden Tabelle aufgelistet:
| Eigenschaft | Typ | Wert [Einheit] |
|---|---|---|
| Standardbildungsenthalpie | ΔfH0gas ΔfH0liquid |
−191,4 kJ·mol−1[9] −226,7 kJ·mol−1[9] |
| Verbrennungsenthalpie | ΔcH0liquid | −4814 kJ·mol−1[9] |
| Wärmekapazität | cp | 219,58 J·mol−1·K−1 (25 °C)[10] als Flüssigkeit |
| Schmelzenthalpie | ΔfH0 | 9,548 kJ·mol−1[10] beim Schmelzpunkt |
| Schmelzentropie | ΔfS0 | 61,77 kJ·mol−1[10] beim Schmelzpunkt |
| Verdampfungsenthalpie | ΔVH0 | 31,12 kJ·mol−1[11] beim Normaldrucksiedepunkt 35,32 kJ·mol−1[11] bei 25 °C |
| Kritische Temperatur | TC | 267,4 °C[12] |
| Kritischer Druck | PC | 28,9 bar[12] |
| Kritisches Volumen | VC | 0,416 l·mol−1[12] |
| Kritische Dichte | ρC | 2,41 mol·l−1[12] |
Sicherheitstechnische Kenngrößen
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]3-Ethylpentan bildet leicht entzündliche Dampf-Luft-Gemische. Die Verbindung hat einen Flammpunkt von −18 °C.[1]
Einzelnachweise
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]- ↑ a b c d e f g h i Eintrag zu 3-Ethylpentan in der GESTIS-Stoffdatenbank des IFA, abgerufen am 2. Januar 2024. (JavaScript erforderlich)
- ↑ Streiff, A.J.; Murphy, E.T.; Sedlak, V.A.; Willingham, C.B.; Rossini, F.D.: Purification, Purity, and Freezing Points of 7 Heptanes, 16 Octanes, 6 Pentene, Cyclopentene, and 7 C9H12 Alkylbenzenes of the API-Standard and API-NBS Series in J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. (U. S.) 37 (1946) 331.
- ↑ David R. Lide (Hrsg.): CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. 90. Auflage. (Internet-Version: 2010), CRC Press / Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton FL, Physical Constants of Organic Compounds, S. 3-252.
- ↑ Sachanen, A.N. in The Chemistry of Petroleum Hydrocarbons Band I (Brooks, B.T.), New York 1954, S. 9.
- ↑ Haensel, V.; Donaldson, G.R.: Platforming of Pure Hydrocarbons in Ind. Eng. Chem. 43 (1951) 2102–2104, doi:10.1021/ie50501a036.
- ↑ Blomsma, E.; Martens, J.A.; Jacobs, P.A.: Reaction Mechanisms of Isomerization and Cracking of Heptane on Pd/H-Beta Zeolite in J. Catal. 155 (1995) 141–147, doi:10.1006/jcat.1995.1195.
- ↑ Edgar, G.; Calingaert, G.; Marker, R.E.: The preparation and properties of the isomeric heptanes. Part I. Preparation in J. Am. Chem. Soc. 51 (1929) 1483–1491, doi:10.1021/ja01380a027.
- ↑ Forziati, A.F.; Norris, W.R.; Rossini, F.D.: Vapor Pressures and Boiling Points of Sixty API-NBS Hydrocarbons in J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. (U.S.) 43 (1949) 555–567.
- ↑ a b c Davies, G.F.; Gilbert, E.C.: Heats of combustion and formation of the nine isomeric heptanes in the liquid state in J. Am. Chem. Soc. 63 (1941) 2730–2732, doi:10.1021/ja01855a064.
- ↑ a b c Huffman, H.M.; Gross, M.E.; Scott, D.W.; McCullough, I.P.: Low temperature thermodynamic properties of six isomeric heptanes in J. Phys. Chem. 65 (1961) 495-503, doi:10.1021/j100821a026.
- ↑ a b Majer, V.; Svoboda, V.: Enthalpies of Vaporization of Organic Compounds: A Critical Review and Data Compilation, Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, 1985, S. 300.
- ↑ a b c d Daubert, T. E.: Vapor-Liquid Critical Properties of Elements and Compounds. 5. Branched Alkanes and Cycloalkanes in J. Chem. Eng. Data 41 (1996) 365–372, doi:10.1021/je9501548.



