Liste der Liganden-Abkürzungen
(Weitergeleitet von Liganden-Abkürzungen)
Auf dieser Seite werden allgemein gebräuchliche Abkürzungen für Liganden in der Chemie zusammengestellt. Als Ligand wird hier allgemein eine Gruppe von Atomen oder einzelne Atomen verstanden, die an ein zentrales Teilchen koordiniert sind. Die Abkürzungen werden im Allgemeinen in die Strukturformel mit einbezogen.
Auch Aminosäuren können als Liganden koordinieren. Diese können mit dem Dreibuchstabencode bezeichnet werden.
| Abkürzung | Name | maximale Zähnigkeit (κ) | maximale Haptizität (η) | Ladung | Struktur |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetylacetonat | 2 | −1 | 
| ||
| Acetonitril | 1 | 0 | 
| ||
| Acridin |  | ||||
| Acetat | 1 | −1 | 
| ||
| 2-(2-Aminoethylamino)ethanol | 3 | 0 | 
| ||
| 2-Picolylamin | 2 | 0 |  | ||
| 4-Aminopyridin (Fampridin) |  | ||||
| Wasser | 1 | 0 | 
| ||
| Biuret | 
| ||||
| 2,2′-bis(diphenylphosphino)-6,6′-dimethoxy-1,1′-biphenyl | 
| ||||
| 2,2'-Binaphthyldiphenyldiphosphin | 2 | 0 | 
| ||
| 1,2-Bis[4,5-dihydro-3H-binaphtho[1,2-c:2′,1′-e]phosphepino]benzen | |||||
| 1,1′-Bis{4,5-dihydro-3H-dinaphtho[1,2-c: 2′,1′-e]phosphepino}ferrocen | |||||
| 4,4′-Di-tert-butyl-4,4′,5,5′-tetrahydro-3,3′-bis-3H-dinaphtho[2,1-c:1′,2′-e]phosphepin | |||||
| 4,5-Dihydro-3H-dinaphtho[2,1-c;1′,2′-e]phosphepin | |||||
| 1,1′-Bi-2-naphthol | 2 | −2 | 
| ||
| 5,5'-Bis-tert-butyl-bipyridin | 2 | 0 | 
| ||
| 5,5'-Bis-tert-butyl-bipyridin | 2 | 0 | |||
| Benzylmethylphenylphosphin | 1 | 0 | |||
| Bis(2-((S)-4-iso-propyl-4,5-dihydrooxazol-2-yl)phenyl)amin | |||||
| Bis(2-((S)-4-tert-butyl-4,5-dihydrooxazol-2-yl)phenyl)amin | |||||
| Bis(oxazolin)-Liganden | 2 | 0 | 
| ||
| 1,2-Bis(2,5-diethylphospholano)ethan | 2 | 0 | |||
| Butoxycarbonyl-4-diphenylphosphino-2-diphenylphosphinomethyl-pyrrolidin | 
| ||||
| 2,2′-Bipyridin | 2 | 0 | 
| ||
| 2,2′-Bipyridin | 2 | 0 | 
| ||
| Cyclohexyl-o-anisylmethylphosphin | 1 | 0 | |||
| Bis(diphenylphosphino)butan | 2 | 0 | 
| ||
| Tropylium (Cycloheptatrienyl) | 1 | 7 | +1 | 
| |
| Citrat | 3 | −3 | 
| ||
| 1,5-Cyclooctadien | 2 | 4 | 0 | 
| |
| Cycloocten | 1 | 2 | 0 | 
| |
| Cyclooctatetraen | 2 | 4 | 0 | 
| |
| Cyclooctatetraen | 1 | 8 | −2 | 
| |
| Cyclopentadienyl | 1 | 5 | −1 | 
| |
| Pentamethylcyclopentadienyl | 1 | 5 | −1 | 
| |
| Diacetonalkohol | 1 | 0 | 
| ||
| 1,4-Diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octan | 1 | 0 | 
| ||
| Diacetyldioxim |  | ||||
| Dibenzylidenaceton | 2 | 4 | 0 | 
| |
| Dibenzoylmethan | 2 | −1 | 
| ||
| Diethylazodicarboxylat | 
| ||||
| Diethyl-2,6-pyridindicarboxylat | |||||
| Diethylentriamin | 3 | 0 | 
| ||
| O-Isopropyliden-2,3-dihydroxy-1,4-bis(diphenylphosphino)butan | 2 | 0 | 
| ||
| (1R,2R)-Bis[(2-methoxyphenyl)phenylphosphino]ethan | 2 | 0 | 
| ||
| 1,2-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ethan | 2 | 0 | 
| ||
| Dipicolinsäure | 5 | 3 | −2 |  | |
| 4-Dimethylaminopyridin | 1 | 0 | 
| ||
| Dimethyl-2,6-pyridindicarboxylat (Dimethyldipicolinat) | |||||
| Dimethylformamid | 1 | 0 | 
| ||
| Dimethylglyoxim | 2 | −1 | 
| ||
| 1,4,7,10-Tetraazacyclododecan-1,4,7,10-tetraessigsäure | 8 | −4 | 
| ||
| 1,2-Bis[dimethylphosphino]ethan | 2 | 0 | 
| ||
| Neocuproin (2,9-Dimethyl-1,10-phenanthrolin) | 2 | 0 | 
| ||
| Dimethylsulfoxid | 1 | 0 | 
| ||
| (R,R)- & (S,S)-1,2-Diphenylethylene-1,2-diamin | |||||
| Dipivaloylmethan | |||||
| 1,2-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ethan | 2 | 0 | 
| ||
| Bis(diphenylphosphino)methan | 2 | 0 | 
| ||
| 1,3-Bis(diphenylphosphino)propan | 2 | 0 | 
| ||
| Diethylentriamin-Pentaacetat | 8 | −5 | 
| ||
| Bis(2,5-dimethylphospholano)benzol | 2 | 0 | |||
| Ethylendiamintetraacetat | 6 | −4 | 
| ||
| Ethylen-bis(oxyethylennitrilo)-tetraacetat | |||||
| Ethylendiamin | 2 | 0 | |||
| α,α,α′,α′-tetramethyl-1,3-benzenedipropionate (benannt nach Christine G. Espino)[1] | |||||
| Hexafluoracetylaceton | 2 | −1 | 
| ||
| Iminodiessigsäure | 3 | −2 | |||
| Ligand | |||||
| 2,2′-Bis[(N,N-dimethylamino)(phenyl)methyl]-1,1′-bis(dicyclohexylphosphino)ferrocen | |||||
| N-Methyliminodiessigsäure | 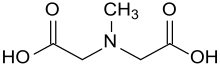
| ||||
| (3,5-Dioxa-4-phosphacyclohepta[2,1-a;3,4-a′]dinapthalen-4-yl)dimethylamin | |||||
| Methylphenyl-n-propylphosphin | |||||
| 1,3-Diketiminat | 2 | −1 | 
| ||
| Bicyclo[2.2.1]hepta-2,5-dienyl | 2 | 4 | 0 | 
| |
| Bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-1-yl | |||||
| 2,3-Bis(diphenylphosphino)-bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-en | |||||
| N-Heterocyclische Carbene | 
| ||||
| Nitrilotriessigsäure | 4 | −3 | 
| ||
| Acetat | 1 | −1 | 
| ||
| tert-Butylat | 1 | −1 | 
| ||
| Ethanolat | 1 | −1 | |||
| Methanolat | 1 | −1 | 
| ||
| Oxalat | 2 | −2 | 
| ||
| 8-Hydroxychinolin | 2 | 0 | 
| ||
| Phenyl o-anisylmethylphosphin | |||||
| Tricyclohexylphosphan | 1 | 0 | 
| ||
| Phthalocyanin | 4 | −2 | 
| ||
| Phenanthrolin | 2 | 0 | 
| ||
| Picolylamin | |||||
| Piperidin | 1 | 0 | 
| ||
| Piperazin |  | ||||
| Porphin | 
| ||||
| Triphenylphosphan | 1 | 0 | 
| ||
| 2-Phenylpyridin | 1 | 0 | |||
| Collidinsäure (2,4,6-Pyridintricarbonsäure) |  | ||||
| ptz | 1-Propyl-1H-tetrazol | ||||
| Pyridyl | 1 | 0 | 
| ||
| Bis(oxazolin)-Liganden | 3 | 0 | 
| ||
| Pyrazin | 1 | 0 | 
| ||
| Quinolin-8-olato | |||||
| Bis(salicyliden)ethylendiaminat | 4 | −2 | 
| ||
| Lösungsmittel (Solvent) | |||||
| 1,4,7-Triazacyclononan | |||||
| α,α,α´,α´-Tetraaryl-1,3-dioxolan-4,5-dimethanol | 2 | −2 | 
| ||
| Tartrat | 4 | −2 | 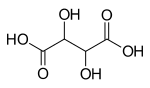
| ||
| 2,4,6-Triamino-1,3,5-triamin |  | ||||
| Ethylendiaminotriacetat | 5 | −3 | |||
| Terpyridin | 3 | 0 | 
| ||
| Triethylentetramin | 4 | 0 | |||
| Triflat | 1 | −1 | 
| ||
| Tetramethylethylendiamin | 2 | 0 | 
| ||
| Tetramethylethylendiamin | 2 | 0 | 
| ||
| Tris(pyrazolyl)borat | 3 | −1 | 
| ||
| Tetraphenylporphyrin | 4 | −2 | 
| ||
| Triphenylphosphantrisulfonat | |||||
| Tris(2-aminoethyl)amin | 4 | 0 | |||
| Triethylentetramin | 4 | 0 | |||
| Triethylentetraminhexaessigsäure | 10 | −6 | 
| ||
| , | Halogenid oder Pseudohalogenid |
Siehe auch
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]Literatur
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]- Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry, IUPAC Recommendations 2005 ("Red Book"), Tabelle VII, Ligand abbreviations, S. 267. (PDF-Datei; 4,14 MB)
Einzelnachweise
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]- ↑ J. Du Bois et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004,126, 47, doi:10.1021/ja0446294.
























































































































