Liste von Säuren
Zur Navigation springen
Zur Suche springen
Die folgende Liste zeigt eine Auswahl von Säuren. Aufgelistet sind
- der gebräuchliche Trivialname
- der IUPAC-Name (die offizielle Bezeichnung)
- die Summenformel oder eine vereinfachte Strukturformel
Die Liste erhebt keinen Anspruch auf Vollständigkeit.
Anorganische Säuren (Auswahl)
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]Säuren der Edelgase
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]| Element | Oxidationszustand des Zentralatomes | Trivialname | Formel | Salze |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xenon | +6 | Xenonsäure | Xenate | |
| +8 | Perxenonsäure | Perxenate |
Säuren der Halogene
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]| Element | Oxidationszustand des Halogenatomes | Trivialname | Formel | Salze | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluor | −1 | Flusssäure | Fluoride | Wässrige Lösung von Fluorwasserstoff | |
| −1 | Hypofluorige Säure | Hypofluorite | |||
| Chlor | −1 | Salzsäure | Chloride | Wässrige Lösung von Chlorwasserstoff | |
| +1 | Hypochlorige Säure | Hypochlorite | |||
| +3 | Chlorige Säure | Chlorite | |||
| +5 | Chlorsäure | Chlorate | |||
| +7 | Perchlorsäure | Perchlorate | |||
| Brom | −1 | Bromwasserstoffsäure | Bromide | ||
| +1 | Hypobromige Säure | Hypobromite | |||
| +3 | Bromige Säure | Bromite | |||
| +5 | Bromsäure | Bromate | |||
| +7 | Perbromsäure | Perbromate | |||
| Iod | −1 | Iodwasserstoffsäure | Iodide | Wässrige Lösung von Iodwasserstoff | |
| +1 | Hypoiodige Säure | Hypoiodite | |||
| +3 | Iodige Säure | Iodite | |||
| +5 | Iodsäure | Iodate | |||
| +7 | Periodsäure | (Metaperiodsäure), (Orthoperiodsäure), (Triperiodsäure) |
Periodate | Es gibt verschiedenartige Periodate, weil es mehrere Periodsäuren gibt. |
Säuren der Chalkogene
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]| Element | Oxidationszustand | Trivialname | Formel | Salze | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schwefel | −2 | Schwefelwasserstoff | Sulfide | ||
| +2 | Sulfoxylsäure | Sulfoxylate | |||
| −1 / +5 | Thioschwefelsäure | Thiosulfate | |||
| +3 | Dithionige Säure | ||||
| +3 / +5 | Dischweflige Säure | Disulfite | |||
| +4 | Schweflige Säure | Sulfite | Entsteht durch Reaktion von Schwefeldioxid mit Wasser | ||
| +5 | Dithionsäure | Dithionate | |||
| +6 | Schwefelsäure | Sulfate | Wird mithilfe von Schwefeltrioxid hergestellt | ||
| +6 | Dischwefelsäure | Disulfate | |||
| +6 | Peroxomonoschwefelsäure | Peroxomonosulfate | |||
| +6 | Peroxodischwefelsäure | Peroxodisulfate | |||
| Selen | −2 | Selenwasserstoff | Selenide | ||
| +4 | Selenige Säure | Selenite | |||
| +6 | Selensäure | Selenate | |||
| Tellur | -2 | Tellurwasserstoff | Telluride | ||
| +4 | Tellurige Säure | Tellurite | |||
| +6 | Tellursäure | Tellurate |
Säuren der Stickstoffgruppe
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]| Element | Oxidationszustand | Trivialname | Formel | Salze | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stickstoff | −2 / −3 / −4 | Stickstoffwasserstoffsäure | Azide | Wird mithilfe von Hydrazin hergestellt | |
| +1 | Hyposalpetrige Säure | Hyponitrite | |||
| +3 | Salpetrige Säure | Nitrite | Wird mithilfe von Stickstoffdioxid hergestellt | ||
| +5 | Salpetersäure | Nitrate | |||
| +5 | Peroxosalpetersäure | Peroxonitrate | |||
| Phosphor | +1 | Phosphinsäure | Phosphinate | ||
| +3 | Phosphonsäure Phosphorigsäure |
Phosphonate Phosphite |
|||
| +5 | Hypodiphosphonsäure | Hypodiphosphonate | |||
| +5 | Diphosphonsäure | Diphosphonate | |||
| +5 | Phosphorsäure | Phosphate | Wird mithilfe von Phosphorpentoxid hergestellt | ||
| +4 | Hypodiphosphorsäure | Hypodiphosphate | |||
| +5 | Diphosphorsäure | Diphosphate | |||
| +5 | Peroxophosphorsäure | Peroxophosphate | |||
| +5 | Peroxodiphosphorsäure | Peroxodiphosphate | |||
| Arsen | +3 | Arsenige Säure | Arsenite | ||
| +5 | Arsensäure | Arsenate | |||
| Antimon | +3 | Antimonige Säure | Antimonite | ||
| +5 | Antimonsäure | Antimonate |
Säuren der Kohlenstoff- und Bor-Gruppe
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]| Element | Oxidationszustand | Trivialname | Formel | Salze | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kohlenstoff | +4 | Kohlensäure | Carbonate | Entsteht durch Reaktion von Kohlenstoffdioxid mit Wasser | |
| Silicium | +4 | Metakieselsäure | Metasilicate | ||
| +4 | Orthokieselsäure | Orthosilicate | |||
| +4 | Orthodikieselsäure | Orthodisilicate | |||
| Bor | +3 | Borsäure | Borate |
Säuren der Übergangsmetalle
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]| Element | Oxidationszustand | Trivialname | Formel | Salze |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gold | +4 | Tetrachlorogoldsäure | Tetrachloroaurate | |
| Iridium | +4 | Hexachloroiridiumsäure | Hexachloroiridate | |
| Platin | +4 | Hexachloroplatinsäure | Hexachloroplatinate | |
| +4 | Platinsäure | Platinate | ||
| Osmium | +4 | Hexachloroosmiumsäure | Hexachloroosmate | |
| Titan | +4 | Hexafluorotitansäure | Hexafluorotitanate | |
| Zirconium | +4 | Hexafluorozirconiumsäure | Hexafluorozirconate | |
| Vanadium | +5 | Vanadiumsäure | Vanadate | |
| Chrom | +6 | Chromsäure | Chromate | |
| +6 | Dichromsäure | Dichromate | ||
| Molybdän | +6 | Molybdänsäure | Molybdate | |
| Wolfram | +6 | Wolframsäure | Wolframate | |
| Mangan | +6 | Mangansäure | Manganate | |
| +7 | Permangansäure | Permanganate | ||
| Rhenium | +7 | Perrheniumsäure | Perrhenate | |
| Technetium | +7 | Pertechnetiumsäure | Pertechnetate |
Sonstige Säuren
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]| Trivialname | Formel | Salze |
|---|---|---|
| Amidosulfonsäure | H2N-SO2-OH | Amidosulfonate |
| Cyanwasserstoff | HCN | Cyanide |
| Cyansäure | HOCN | Cyanate |
| Fulminsäure / Knallsäure | HCNO | Fulminate |
| Isocyansäure | HNCO | Cyanate |
| Isofulminsäure / Isoknallsäure | HONC | Fulminate |
| Thiocyansäure | HSCN | Thiocyanate |
| Königswasser | Mischung aus 3 Teilen Salzsäure und 1 Teil Salpetersäure |
Organische Säuren (Auswahl)
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]Kurzkettige aliphatische Carbonsäuren und Derivate
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]| Ausgangsalkan | gesättigte Carbonsäure | ungesättigte Carbonsäuren | gesättigte Dicarbonsäuren | ungesättigte Dicarbonsäuren | Sauerstoffhaltige Derivate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methan (CH4) | Ameisensäure HCOOH |
– | – | – | – |
| Ethan (C2H6) | Essigsäure H3C-COOH |
– | Oxalsäure HOOC-COOH |
– | Glycolsäure HOCH2-COOH Glyoxalsäure O=CH-COOH |
| Propan (C3H8) | Propionsäure H3C-CH2-COOH |
Acrylsäure H2C=CH-COOH |
Malonsäure HOOC-CH2-COOH |
– | Milchsäure H3C-CH(OH)-COOH Tartronsäure HOOC-CH(OH)-COOH |
| n-Butan (C4H10) | Buttersäure H3C-(CH2)2-COOH |
Crotonsäure H3C-CH=CH-COOH (cis-Stellung) Isocrotonsäure H3C-CH=CH-COOH (trans-Stellung) Vinylessigsäure H2C=CH-CH2-COOH |
Bernsteinsäure HOOC-(CH2)2-COOH |
Maleinsäure HOOC-CH=CH-COOH (cis-Stellung) Fumarsäure HOOC-CH=CH-COOH (trans-Stellung) |
Gamma-Hydroxybuttersäure HO-(CH2)3-COOH Äpfelsäure HOOC-CH(OH)-CH2-COOH Weinsäure HOOC-CH(OH)-CH(OH)-COOH Oxalessigsäure HOOC-CH2-CO-COOH Quadratsäure C4H2O4 |
| n-Pentan (C5H12) | Valeriansäure H3C-(CH2)3-COOH |
Allylessigsäure H2C=CH-(CH2)2-COOH |
Glutarsäure HOOC-(CH2)3-COOH |
– | α-Ketoglutarsäure HOOC-CH2-CH2-CO-COOH Zitronensäure HOOC-CH2-C(OH)(COOH)-CH2-COOH Isocitronensäure HOOC-CH(OH)-CH(COOH)-CH2-COOH Aconitsäure HOOC-CH=CH(COOH)-CH2-COOH |
| n-Hexan (C6H14) | Capronsäure H3C-(CH2)4-COOH |
Sorbinsäure H3C-CH=CH-CH=CH-COOH (trans-Stellung) |
Adipinsäure HOOC-(CH2)4-COOH |
– | Gluconsäure HO-CH2-(CH(OH))4-COOH |
| n-Heptan (C7H16) | Önanthsäure H3C-(CH2)5-COOH |
– | Pimelinsäure HOOC-(CH2)5-COOH |
– | – |
| n-Octan (C8H18) | Caprylsäure H3C-(CH2)6-COOH |
– | Suberinsäure HOOC-(CH2)6-COOH |
– | – |
| n-Nonan (C9H20) | Pelargonsäure H3C-(CH2)7-COOH |
– | Azelainsäure HOOC-(CH2)7-COOH |
– | – |
| n-Decan (C10H22) | Caprinsäure H3C-(CH2)8-COOH |
– | Sebacinsäure HOOC-(CH2)8-COOH |
– | – |
Langkettige aliphatische Carbonsäuren und Derivate
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]Weitere Carbonsäuren und Derivate
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]- Hier sind nur Aminosäuren mit einem sauren Charakter angegeben.
| Trivialname (IUPAC-Name) | Formel | Salze |
|---|---|---|
| Asparaginsäure | HOOC-CH2-CH(NH2)-COOH | Aspartate |
| Carbamidsäure | H2N-COOH | Carbamate |
| Glutaminsäure | HOOC-CH2-CH2-CH(NH2)-COOH | Glutamate |
Weitere Carbonsäurederivate
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]- Hier sind weitere Derivate der Carbonsäuren angegeben, welche Fremdatome wie Halogene, Schwefel oder Phosphor enthalten.
| Trivialname (IUPAC-Name) | Formel | Salze |
|---|---|---|
| Chloressigsäure | CH2Cl-COOH | Monochloracetate |
| Fluoressigsäure | CH2F-COOH | Monofluoracetate |
| Trichloressigsäure | Cl3C-COOH | Trichloracetate |
| Trifluoressigsäure | F3C-COOH | Trifluoracetate |
Alphabetische Liste von Trivialnamen (Auswahl)
[Bearbeiten | Quelltext bearbeiten]- Anmerkung: Sehr lange IUPAC-Namen sind hier teilweise weggelassen worden. Sie können im Artikel zur jeweiligen Säure nachgelesen werden.
| Trivialname | IUPAC-Name | Stäbchenmodell | Strukturformel | Formel | Charakteristische Elemente | Säurekonstanten (pKs) | Salze | Bemerkungen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abietinsäure | Abieta-7,14-dien-19-carbonsäure | 
|

|
C20H30O2 | Kohlenstoff | Abietate | Bestandteil von Baumharz | |
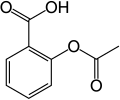
| Acetylsalicylsäure | 2-(Acetyloxy)benzoesäure | 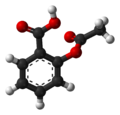
|
|
HOOC-C6H4-COOCH3 | Kohlenstoff | 3,49 | Acetylsalicylate | Der medizinische Wirkstoff Aspirin. Ein Derivat der Salicylsäure und der Benzoesäure. |
| Acrylsäure | Propensäure | 
|

|
H2C=CH-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,26 | Acrylate | Eine einfach ungesättigte Carbonsäure |
| Adipinsäure | Hexandisäure | 
|
HOOC-(CH2)4-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,43; 5,42 | Adipate | Eine Dicarbonsäure | |
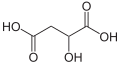
| Äpfelsäure | 2-Hydroxybutandisäure | 
|
|
HOOC-CH2-CH(OH)-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 3,46; 5,10 | Malate | Eine Dicarbonsäure |
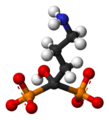
| Alendronsäure | 4-Amino-1-hydroxybutyliden -Diphosphonsäure |
|

|
C4H13NO7P2 | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff, Phosphor | 2,72 | Alendronate | |
| Ameisensäure | Methansäure | 
|

|
HCOOH | Kohlenstoff | 3,77 | Formiate | Die einfachsteCarbonsäure und Alkansäure |
| Amidosulfonsäure | Amidoschwefelsäure |  
|
H2N-SO2-OH | Stickstoff, Schwefel | 1,0 | Amidosulfonate | Kommt beiStandardbedingungen nur als Zwitterion+H3N-SO3− vor | |
| Antimonige Säure | H3SbO3 | Antimon | Antimonite | |||||
| Antimonsäure | Hexahydroxoantimon(V)-säure | 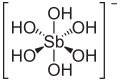
|
H[Sb(OH)6] | Antimon | 2,55 | Antimonate | ||
| Arachidonsäure | 5,8,11,14-Eicosatetraensäure | 
|

|
C20H32O2 | Kohlenstoff | 4,752 | ||
| Arachinsäure | Eicosansäure | H3C-(CH2)18-COOH | Kohlenstoff | Arachinoate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | |||
| Arsenige Säure | Trihydrogenarsenit | 
|

|
H3AsO3 | Arsen | Arsenite | ||
| Arsensäure | Trihydrogenarsenat | 
|

|
H3AsO4 | Arsen | 2,26; 6,76; 11,29 | Arsenate | |
| Ascorbinsäure | (5R)-5-[(1S)-1,2-Dihydroxyethyl]-
3,4-dihydroxy-5-hydrofuran-2-on |

|

|
C6H8O6 | Kohlenstoff | 4,25 | Ascorbate | Wird auch Vitamin C genannt |
| Barbitursäure | 2,4,6-Trihydroxy-pyrimidin | 
|

|
C4H4N2O3 | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | 4,01 | Barbiturate | Ein Derivat des Harnstoffs |
| Behensäure | Docosansäure | H3C-(CH2)20-COOH | Kohlenstoff | Behenate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | |||
| Benzoesäure | Benzolcarbonsäure | 
|

|
C6H5COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,2 | Benzoate | Ein Derivat von Benzol |
| Bernsteinsäure | Butandisäure | 
|

|
HOOC-(CH2)2-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,16; 5,61 | Succinate | Eine Dicarbonsäure |
| Blausäure | Cyanwasserstoff | 
|
HCN | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | 9,40 | Cyanide | ||
| Bicinchoninsäure | 2,2'-Bichinolin-4,4'-dicarbonsäure | 
|
C20H12N2O4 | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | Eine Dicarbonsäure | |||
| Borsäure | Trihydrogenborat | 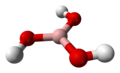
|
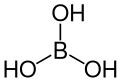
|
H3BO3 | Bor | 9,24; 12,4; 13,3 | Borate | |
| Brenztraubensäure | 2-Oxopropansäure | 
|

|
CH3-CO-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 2,49 | Pyruvate | Die einfachste Ketosäure |
| Bromige Säure | Hydrogenbromit | 
|
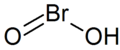
|
HBrO2 | Brom | Bromite | ||
| Bromsäure | Hydrogenbromat | 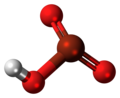
|

|
HBrO3 | Brom | −2,0 | Bromate | |
| Bromwasserstoffsäure | Hydrogenbromid | 
|
HBr(aq) | Brom | −9,0 | Bromide | Wässrige Lösung von Bromwasserstoff. Eine Supersäure. | |
| Buttersäure | Butansäure | 
|

|
H3C-(CH2)2-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,82 | Butyrate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure |
| Caprinsäure | Decansäure | H3C-(CH2)8-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,9 | Decanoate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | ||
| Capronsäure | Hexansäure | H3C-(CH2)4-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,85 | Hexanoate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | ||
| Caprylsäure | Octansäure | H3C-(CH2)6-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,89 | Caprate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | ||
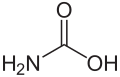
| Carbaminsäure | Aminomethansäure | 
|
|
H2N-COOH | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | Carbamate | Eine Aminosäure | |
| Cerotinsäure | Hexacosansäure | 
|
C25H51COOH | Kohlenstoff | Hexacosanoate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | ||
| Chinasäure | 1,3,4,5-Tetrahydroxy-cyclohexan-1-carbonsäure | 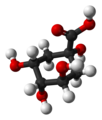
|

|
C6H7(OH)4COOH | Kohlenstoff | |||
| Chloressigsäure | Monochlorethansäure | 
|

|
H2ClC-COOH | Kohlenstoff, Chlor | 2,87 | Monochloracetate | |
| Chlorige Säure | Hydrogenchlorit | 
|
HClO2 | Chlor | 1,97 | Chlorite | ||
| Chlorsäure | Hydrogenchlorat | 
|

|
HClO3 | Chlor | −2,7 | Chlorate | |
| Chorisminsäure | (3R)-trans-(1-Carboxyvinyloxy) -4-hydroxy-1,5-cyclohexadien-1-carbonsäure |

|
C10H10O6 | Kohlenstoff | Chorismate | |||
| Chromsäure | Dihydrogenchromat | 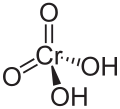
|
H2CrO4 | Chrom | −0,8; 1,6 | Chromate | ||
| Citronensäure | 3-Carboxy-3-hydroxy-pentan-1,5-disäure | 
|

|
HOOC-CH2-C(OH)(COOH)-CH2-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 3,13; 4,76; 6,4 | Citrate | Eine Tricarbonsäure |
| Clavulansäure | – | 
|

|
C8H9NO5 | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | Clavulanate | ||
| Cyansäure | Hydrogencyanat | 
|

|
HOCN | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | Cyanate | ||
| Dichromsäure | Dihydrogendichromat | 
|
H2Cr2O7 | Chrom | Dichromate | |||
| Diphosphonsäure | Hydrogendiphosphonat | H4P2O5 | Phosphor | Diphosphonate | ||||
| Diphosphorsäure | Hydrogendiphosphate | 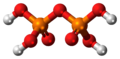
|

|
H4P2O7 | Phosphor | 1,52; 2,36; 6,60; 9,25 | Diphosphate | |
| Dischwefelsäure | Dihydrogendisulfat | 
|

|
H2S2O7 | Schwefel | Disulfate | ||
| Ellagsäure | – | 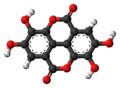
|

|
C14H6O8 | Kohlenstoff | |||
| Erucasäure | cis-13-Docosensäure | H3C-(CH2)7-CH=CH-(CH2)11-COOH | Kohlenstoff | Eine einfach ungesättigte Fettsäure | ||||
| Essigsäure | Ethansäure | 
|

|
CH3COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,76 | Acetate | Eine Alkansäure |
| Fluoressigsäure | Monofluorethansäure | 
|

|
CH2F-COOH | Kohlenstoff, Fluor | 2,59 | Monofluoracetate | |
| Fluorsulfonsäure | 
|

|
HSO3F | Schwefel, Fluor | −10,0 | Eine Supersäure | ||
| Flusssäure | Fluorwasserstoffsäure/Hydrogenfluorid | 
|
HF(aq) | Fluor | 3,17 | Fluoride | Wässrige Lösung von Fluorwasserstoff | |
| Fumarsäure | (2E)-But-2-endisäure | 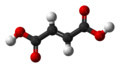
|

|
HOOC-CH=CH-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 3,02; 4,38 | Fumarate | Eine einfach ungesättigte Dicarbonsäure |
| Fusarinsäure | 5-Butyl-pyridin-2-carbonsäure | 
|

|
C10H13NO2 | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | |||
| Fusidinsäure | – | 
|
C31H48O6 | Kohlenstoff | Fusidate | |||
| Gallussäure | 3,4,5-Trihydroxybenzoesäure | 
|

|
C7H6O5 | Kohlenstoff | Gallate | ||
| Gamma-Aminobuttersäure | 4-Aminobutansäure | 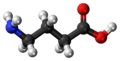
|
H2N-(CH2)3-COOH | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | 4,05 | Eine Aminosäure | ||
| Gamma-Hydroxybuttersäure | 4-Hydroxybutansäure | 
|
HO-(CH2)3-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4-Hydroxybutyrate | |||
| Gondosäure | Eicos-11-ensäure | 
|
H3C-(CH2)7-CH=CH-(CH2)9-COOH | Kohlenstoff | Eine einfach ungesättigte Fettsäure | |||
| Glucarsäure | (2S,3S,4S,5R)-2,3,4,5-Tetrahydroxyhexan-1,6-disäure | 
|
C6H10O8 | Kohlenstoff | Glucarate | Eine Dicarbonsäure | ||
| Gluconsäure | 2,3,4,5,6-Pentahydroxyhexansäure | 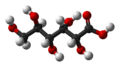
|
C6H12O7 | Kohlenstoff | Gluconate | |||
| Glutarsäure | Pentandisäure | 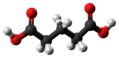
|
HOOC-(CH2)3-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,32; 5,42 | Glutarate | Eine Dicarbonsäure | |
| Glycolsäure | Hydroxyethansäure | 
|

|
HOCH2-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 3,83 | Glycolate | |
| Glyoxalsäure | Ethanalsäure | 
|

|
O=CH-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 3,18; 3,32 | Glyoxylate | |
| Harnsäure | 2,6,8-Trihydroxypurin | 
|
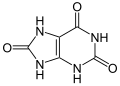
|
C5H4N4O3 | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | 5,75 | Urate | |
| Hexachloroiridiumsäure | Dihydrogenhexachloriridat | H2[IrCl6] | Iridium, Chlor | Hexachloroiridate | ||||
| Hexachloroosmiumsäure | Dihydrogenhexachlorosmat | H2[OsCl6] | Iridium, Chlor | Hexachloroosmate | ||||
| Hexachloroplatinsäure | Dihydrogenhexachlorplatinat | H2[PtCl6] | Platin, Chlor | Hexachloroplatinate | ||||
| Hexafluorantimonsäure | H[SbF6] | Antimon, Fluor | ||||||
| Hexafluorotitansäure | Dihydrogenhexafluorotitanat | 
|
H2[TiF6] | Titan, Fluor | Hexafluorotitanate | |||
| Hexafluorozirconiumsäure | Dihydrogenhexafluorozirconat | H2[ZrF6] | Zirconium, Fluor | Hexafluorozirconate | ||||
| Hippursäure | – | 
|
C9H9NO3 | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | ||||
| Hypochlorige Säure | Hydrogenhypochlorit | 
|

|
HClO | Chlor | 7,54 | Hypochlorite | |
| Hypodiphosphonsäure | Tetrahydrogenhypodiphosphonat | H4P2O4 | Phosphor | Hypodiphosphonate | ||||
| Hypodiphosphorsäure | Tetrahydrogenhypodiphosphat | H4P2O6 | Phosphor | Hypodiphosphate | ||||
| Hyposalpetrige Säure | Dihydrogenhyponitrit | H2N2O2 | Stickstoff | 7,21; 11,54 | Hyponitrite | |||
| Ibotensäure | α-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-isoxazolessigsäure | 
|
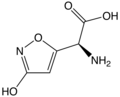
|
C5H6N2O4 | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | Ein Pilzgift, das unter anderem im Fliegenpilz enthalten ist | ||
| Indol-3-essigsäure | 1H-Indol-3-Ethansäure | 
|

|
C10H9NO2 | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | 4,75 | ||
| Iodsäure | Hydrogeniodat | 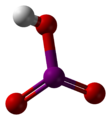
|
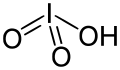
|
HIO3 | Iod | 0,804 | Iodate | |
| Iodwasserstoffsäure | Hydrogeniodid | HI(aq) | Iod | −10,0 | Iodide | Wässrige Lösung von Iodwasserstoff. Eine Supersäure. | ||
| Isocitronensäure | 3-Carboxy-2-hydroxy-pentan-1,5-disäure | 
|
C6H8O7 | Kohlenstoff | Isocitrate | Eine Tricarbonsäure | ||
| Isocyansäure | Hydrogenisocyanat | 
|
HNCO | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | 3,92 | Cyanate | ||
| Isophthalsäure | 1,3-Benzoldicarbonsäure | 
|
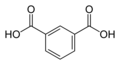
|
C8H6O4 | Kohlenstoff | 3,62; 4,60 | Isophtalate | Eine Dicarbonsäure |
| α-Ketoglutarsäure | 2-Oxopentandisäure | 
|

|
C5H6O5 | Kohlenstoff | α-Ketoglutarate | Eine Dicarbonsäure und Ketosäure | |
| Kieselsäure | H4SiO4 | Silicium | Silicate | Es gibt mehrere Kieselsäuren. | ||||
| Knallsäure | Oxidoazaniumylidynemethan | HCNO | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | Fulminate | ||||
| Königswasser | – | Mischung aus 3 Teilen Salzsäure und 1 Teil Salpetersäure | ||||||
| Kohlensäure | Dihydrogencarbonat | 
|
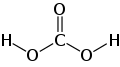
|
H2CO3 | Kohlenstoff | 3,6; 10,3 | Carbonate | Entsteht durch Reaktion von Kohlenstoffdioxid mit Wasser |
| Laurinsäure | Dodecansäure | H3C-(CH2)10-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 5,3 | Laurate | |||
| Lignocerinsäure | Tetracosansäure | H3C-(CH2)22-COOH | Kohlenstoff | Lignocerate | ||||
| α-Linolensäure | (all-cis)-Octadeca-9,12,15-triensäure | 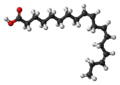
|
C18H30O2 | Kohlenstoff | Eine dreifach ungesättigte Fettsäure | |||
| Linolsäure | (cis,cis)-Octadeca-9,12-diensäure | C18H32O2 | Kohlenstoff | 4,77 | Linoleate | |||
| Magische Säure | – | Mischung aus Fluorsulfonsäure und Antimon(V)-fluorid | ||||||
| Maleinsäure | (2Z)-But-2-endisäure | 
|

|
HOOC-CH=CH-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 1,9; 6,5 | Maleate | Eine einfach ungesättigte Dicarbonsäure |
| Malonsäure | Propandisäure | 
|
HOOC-CH2-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 2,83; 5,69 | Malonate | Eine Dicarbonsäure, die in Zuckerrüben enthalten ist | |
| Mandelsäure | 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylethansäure | 
|

|
C8H8O3 | Kohlenstoff | 3,37 | ||
| Mangansäure | Hydrogenmanganat | H2MnO4 | Mangan | Manganate | ||||
| Margarinsäure | Heptadecansäure | H3C-(CH2)15-COOH | Kohlenstoff | Heptadecanoate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | |||
| Melissinsäure | Triacontansäure | C29H59COOH | Kohlenstoff | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | ||||
| Metakieselsäure | – | H2SiO3 | Silicium | Metasilicate | Eine von mehreren Kieselsäuren | |||
| Methansulfonsäure | – | 
|

|
CH3S-O3H | Kohlenstoff, Schwefel | −1,9 | Mesilate | |
| Milchsäure | 2-Hydroxypropansäure | 
|
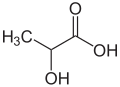
|
H3C-CH(OH)-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 3,90 | Lactate | Bildet wegen ihrer optischen Aktivität die Entantiomere L-Milchsäure und D-Milchsäure |
| Molybdänsäure | Dihydrogenmolybdat | 
|
H2MoO4 | Molybdän | 3,7; 3,9 | Molybdate | ||
| Montansäure | Octacosansäure | C27H55COOH | Kohlenstoff | Montanoate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | |||
| Myristinsäure | Tetradecansäure | H3C-(CH2)12-COOH | Kohlenstoff | Myristate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | |||
| N-Acetylneuraminsäure | – | 
|
C10H19NO9 | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | ||||
| Nervonsäure | Delta-15-cis-Tetracosensäure | H3C-(CH2)7-CH=CH-(CH2)13-COOH | Kohlenstoff | Eine einfach ungesättigte Fettsäure | ||||
| Ölsäure | (9Z)-Octadec-9-ensäure | H3C-(CH2)7-CH=CH-(CH2)7-COOH | Kohlenstoff | Oleate | Eine einfach ungesättigte Fettsäure | |||
| Önanthsäure | Heptansäure | H3C-(CH2)5-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,89 | Heptanoate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | ||
| Orthodikieselsäure | Hexahydrogendisilicat | 
|
H6Si2O7 | Silicium | Orthodisilicate | Eine von mehreren Kieselsäuren | ||
| Orthokieselsäure | Tetrahydrogensilicat | H4SiO4 | Silicium | Orthosilicate | Eine von mehreren Kieselsäuren | |||
| Oxalessigsäure | 2-Oxo-butandisäure | 
|

|
HOOC-CH2-CO-COOH | Kohlenstoff | Oxalacetate | Eine Dicarbonsäure | |
| Oxalsäure | Ethandisäure | 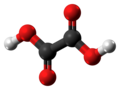
|
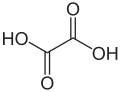
|
HOOC-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 1,23; 4,19 | Oxalate | Die einfachsteDicarbonsäure |
| Palmitinsäure | Hexadecansäure | H3C-(CH2)14-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,75 | Palmitate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | ||
| Palmitoleinsäure | (9Z)-Hexadece-9-nsäure | H3C-(CH2)5-CH=CH-(CH2)7-COOH | Kohlenstoff | Eine einfach ungesättigte Fettsäure | ||||
| Pelargonsäure | Nonansäure | H3C-(CH2)7-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,96 | Pelargonate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | ||
| Perchlorsäure | Hydrogenperchlorat | 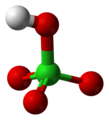
|

|
HClO4 | Chlor | −10,0 | Perchlorate | Eine Supersäure |
| Permangansäure | Dihydrogenpermanganat | H2MnO4 | Mangan | Permanganate | ||||
| Peroxodischwefelsäure | Dihydrogendipersulfat | 
|
H2S2O8 | Schwefel | Peroxodisulfate | |||
| Peroxodiphosphorsäure | Tetrahydrogenperoxodiphosphat | H4P2O8 | Phosphor | Peroxodiphosphate | ||||
| Peroxophosphorsäure | Trihydrogenperoxophosphat | H3PO5 | Phosphor | Peroxophosphate | ||||
| Peroxosalpetersäure | Hydrogenpernitrat | 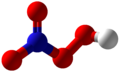
|

|
HNO4 | Stickstoff | Pernitrate | ||
| Perrheniumsäure | Hydrogenperrhenat | 
|

|
HReO4 | Rhenium | −1,25 | Perrhenate | |
| Pertechnetiumsäure | Hydrogenpertechnetat | 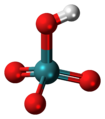
|
HTcO4 | Technetium | Pertechnetate | |||
| Perxenonsäure | Tetrahydrogenperxenat | 
|
H4XeO6 | Xenon | Perxenate | Enthält das Edelgas Xenon | ||
| Phenylessigsäure | 1-Benzolethansäure | 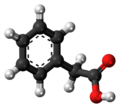
|

|
C8H8O2 | Kohlenstoff | 4,28 | ||
| Phosphinsäure | Trihydrogenphosphinat | 
|

|
H3PO2 | Phosphor | 2,0; 2,23 | Phosphinate | |
| Phosphonsäure | Trihydrogenphosphonat | 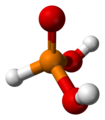
|

|
H3PO3 | Phosphor | 2,0; 6,59 | Phosphonate | |
| Phosphorsäure | Trihydrogenphosphat | 
|

|
H3PO4 | Phosphor | 2,16; 7,21; 12,32 | Phosphate | Wird mithilfe von Phosphorpentoxid hergestellt |
| Phthalsäure | 1,2-Benzoldicarbonsäure | 
|

|
C8H6O4 | Kohlenstoff | 2,95; 5,41 | Phthalate | Eine Dicarbonsäure |
| Pikrinsäure | 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol | 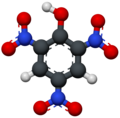
|

|
C6H3N3O7 | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | 0,29 | Pikrate | |
| Pimelinsäure | Heptandisäure | 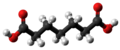
|
C7H12O4 | Kohlenstoff | 4,47; 5,52 | Pimelate | ||
| Platinsäure | Dihydrogenhexahydroxoplatinat(VI) | H2Pt(OH)6 | Platin | Platinate | ||||
| Propionsäure | Propansäure | 
|
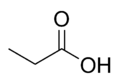
|
H3C-CH2-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,87 | Propionate | Eine Alkansäure |
| Quadratsäure | 3,4-Dihydroxycyclobut-3-en-1,2-dion | 
|
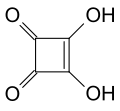
|
C4H2O4 | Kohlenstoff | 1,5; 3,4 | Quadratate | Ein Derivat des Cyclobutens. Eine organische Säure ohne Carboxygruppe. |
| Ricinolsäure | 12-Hydroxy-(9Z)-octadec-9-ensäure | 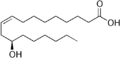
|
C18H34O3 | Kohlenstoff | ||||
| Salicylsäure | 2-Hydroxybenzoesäure | 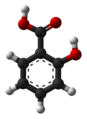
|

|
C7H6O3 | Kohlenstoff | 2,75; 12,38 | Salicylate | Ist der Benzoesäure sehr ähnlich |
| Salpetersäure | Hydrogennitrat | 
|
HNO3 | Stickstoff | −1,37 | Nitrate | Bei dieser Verbindung tritt Mesomerie auf. | |
| Salpetrige Säure | Hydrogennitrit |  |
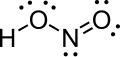
|
HNO2 | Stickstoff | 3,29 | Nitrite | Wird mithilfe von Stickstoffdioxid hergestellt |
| Salzsäure | Chlorwasserstoffsäure/Hydrogenchlorid | 
|
HCl(aq) | Chlor | −5,9 | Chloride | Wässrige Lösung von Chlorwasserstoff. Eine Supersäure. | |
| Schwefelsäure | Dihydrogensulfat | 
|

|
H2SO4 | Schwefel | −3,0; 1,9 | Sulfate | Wird mithilfe von Schwefeltrioxid hergestellt |
| Schwefelwasserstoff | Dihydrogensulfid | 
|

|
H2S | Schwefel | 7,00; 12,92 | Sulfide | |
| Schweflige Säure | Dihydrogensulfit | 
|

|
H2SO3 | Schwefel | 1,81; 6,99 | Sulfite | Entsteht durch Reaktion von Schwefeldioxid mit Wasser |
| Shikimisäure | 3,4,5-Trihydroxy-1-cyclohexencarbonsäure | 
|

|
C7H10O5 | Kohlenstoff | 4,15 | Shikimate | |
| Sorbinsäure | (2E,4E)-2,4-Hexadiensäure | 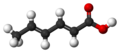
|
C6H8O2 | Kohlenstoff | 4,76 | Sorbate | Eine zweifach ungesättigte Carbonsäure | |
| Stearinsäure | Octadecansäure | H3C-(CH2)16-COOH | Kohlenstoff | Stearate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure | |||
| Stickstoffwasserstoffsäure | Hydrogenazid | 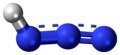
|
HN3 | Stickstoff | 4,6; 7,9 | Azide | Wird mithilfe von Hydrazin hergestellt. Bei dieser Verbindung tritt Mesomerie auf. | |
| Styphninsäure | 2,4,6-Trinitro-1,3-hydroxybenzol | 
|

|
C6H3N3O8 | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | Styphnate | Eine organische Säure ohne Carboxygruppe | |
| Sulfanilsäure | 4-Amino-1-benzolsulfonsäure | 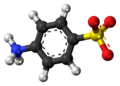
|

|
C6H7NO3S | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | 3,23 | Eine organische Säure ohne Carboxygruppe | |
| Tellursäure | Hexahydrogentellurat | 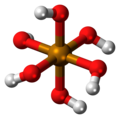
|

|
H6TeO6 | Tellur | 7,70; 10,95 | Tellurate | |
| Terephthalsäure | Benzol-1,4-dicarbonsäure | 
|
C8H6O4 | Stickstoff | 3,54; 4,46 | Terephtalate | Eine Dicarbonsäure | |
| Tetrachlorogoldsäure | Hydrogentetrachloroaurat | 
|
H[AuCl4] | Gold, Chlor | Tetrachloroaurate | |||
| Tetrahydrofolsäure | N-[(6S)-5,6,7,8-Tetrahydropteroyl] -L-glutaminsäure |
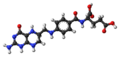
|
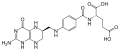
|
C19H23N7O6 | Kohlenstoff, Stickstoff | 3,51 | Eine Dicarbonsäure | |
| Thioschwefelsäure | Dihydrogenthiosulfat | 
|

|
H2S2O3 | Schwefel | 0,6; 1,74 | Thiosulfate | |
| Trichloressigsäure | Trichlorethansäure | 
|

|
Cl3C-COOH | Kohlenstoff, Chlor | 0,65 | Trichloracetate | |
| Trifluormethansulfonsäure | 
|

|
CF3SO3H | Kohlenstoff, Schwefel, Fluor | −20,0 | Triflate | Eine der stärksten Supersäuren | |
| Trifluoressigsäure | Trifluorethansäure | 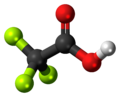
|

|
F3C-COOH | Kohlenstoff, Fluor | 0,23 | Trifluoracetate | |
| Trikieselsäure | (HO)3Si–O–Si(OH)2–O–Si(OH)3. | Silicium | Trisilicate | Eine von mehreren Kieselsäuren | ||||
| Valeriansäure | Pentansäure | 
|

|
H3C-(CH2)3-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 4,84 | Valerate | Eine gesättigte Fettsäure und Alkansäure |
| Vanadiumsäure | Hydrogenvanadat | H3VO4 | Vanadium | Vanadate | ||||
| Vulpinsäure | – | 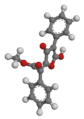
|

|
C19H14O5 | Kohlenstoff | Ein Giftstoff, der in einigen Flechten enthalten ist | ||
| Weinsäure | 2,3-Dihydroxybutandisäure | 
|
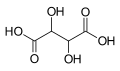
|
HOOC-CH(OH)-CH(OH)-COOH | Kohlenstoff | 2,98; 4,34 | Tartrate | Eine Dicarbonsäure |
| Wolframsäure | Dihydrogenwolfrat | H2WO4 | Wolfram | 3,5; 4,6 | Wolframate | |||
| Xenonsäure | Dihydrogenxenat | 
|

|
H2XeO4 | Xenon | 10,5 | Xenate | Enthält das Edelgas Xenon |
| Zimtsäure | 3-Phenylpropensäure | 
|
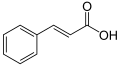
|
C9H8O2 | Kohlenstoff | 4,44 |























































![{\displaystyle {\ce {H[Sb(OH)6]}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e30797e3df56119b39db7c4c3ae7b5a3ae76a236)





![{\displaystyle {\ce {H[AuCl4]}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9a6aeecf36990cee03025ebad8e30c1302f7b29a)
![{\displaystyle {\ce {H2[IrCl6]}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f06b5c8864a7c410556eb8241940f35abbfbc917)
![{\displaystyle {\ce {H2[PtCl6]}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f6db11a0f2bd82fd13760335066370b01133131e)

![{\displaystyle {\ce {H2[OsCl6]}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/68baeca2b2743578e2b42927bf9f707676d5f01e)
![{\displaystyle {\ce {H2[TiF6]}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/213c350639ec33a292ea5a71493f482f1f8ce86e)
![{\displaystyle {\ce {H2[ZrF6]}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8434b0afaa50f73d2e68793c7c28442e82e5e990)








